
Boots are nice in that they provide support to the fracture, allow the children to walk, and can be removed for bathing. This also allows them to heal quickly.ĭepending on the size of the child, most of these fractures are treated by placing the child in a walking boot. Because of this, toddler’s fractures are very stable and do not move out of position. With toddler’s fractures, the calcified, hard portion of the bone is fractured but the thick periosteum is intact. In children’s bones, there is a very thick wrapper surrounding the bone called the periosteum. Even if the X-rays are normal initially, new bone can usually be seen on X-rays that are repeated 2 weeks after the injury as the body heals the fracture.
Usually, there is no swelling or bruising in the area. The physician may be highly suspicious that a fracture exists even if an X-ray is normal but the child has tenderness over the lower leg and/or refuses to put weight on the affected side. How is a Toddler's Fracture Diagnosed?Ī toddler’s fracture may be diagnosed with X-rays, but often the X-rays are normal. The child usually cries and refuses to bear weight on the injured side. The injury or twisting may be minor and go unnoticed. It usually happens because of a twisting injury to the leg. A toddler’s fracture occurs in children 1 to 3 years old.

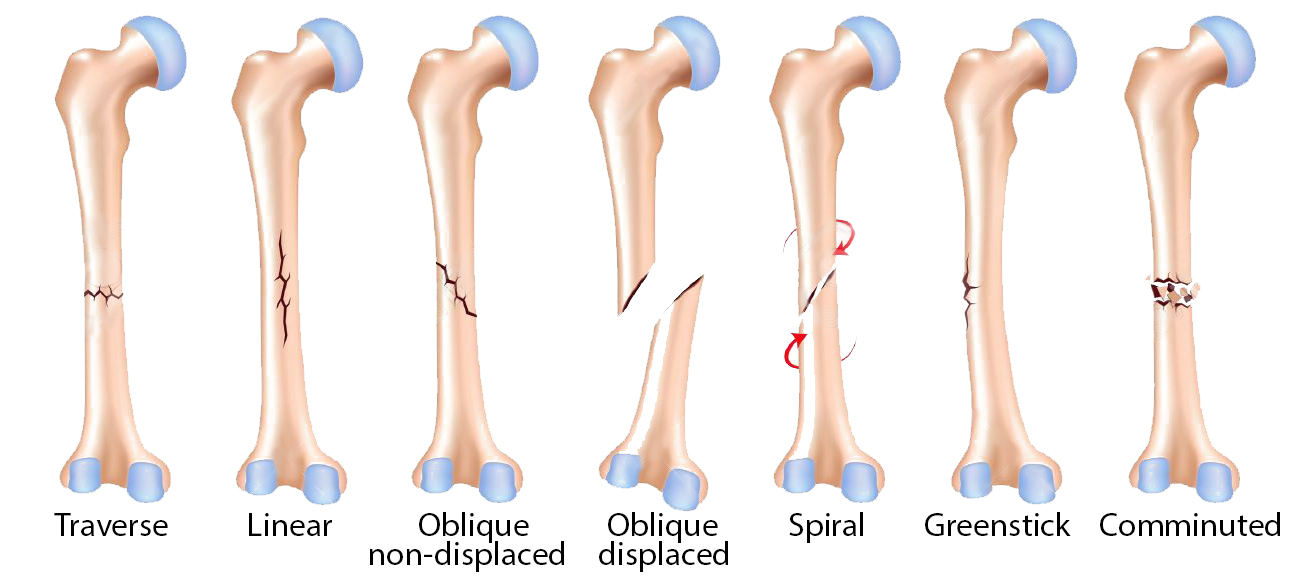
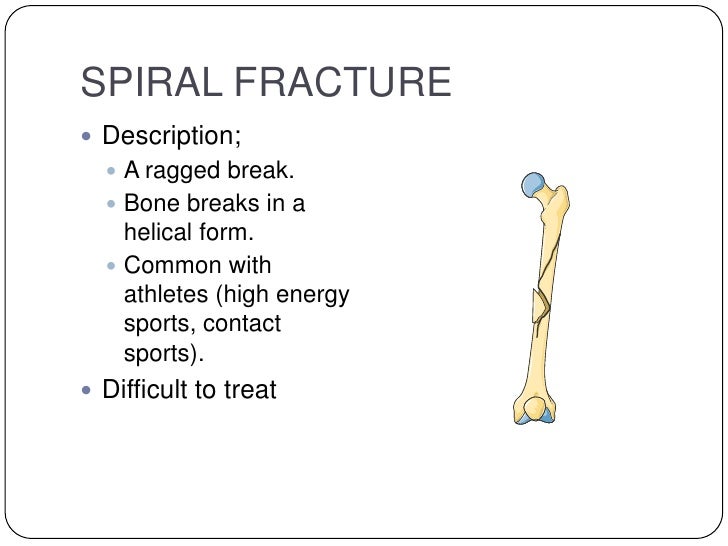
The deep peroneal nerve is responsible for sensation over the first dorsal webspace.A toddler’s fracture is a spiral fracture of the tibia that is perfectly or nearly perfectly aligned. A common result of damage to the deep peroneal nerve is drop foot, in which there is a loss of the capacity to dorsiflex the foot. The deep peroneal nerve innervates the musculature of the anterior compartment and is responsible for the dorsiflexion of the foot and toes. The superficial peroneal nerve also gives sensation to the dorsum of the foot. Damage to this nerve may result in deficits in those movements. The superficial peroneal nerve innervates the musculature of the lateral compartment and is responsible for eversion and, to a much milder degree, plantarflexion of the foot. The triangular shape of the fibula is dictated by the insertion points of the muscles on the shaft. The fibular shaft is an origin for multiple muscles of the leg, including muscles of the anterior compartment (extensor digitorum longus, extensor hallucis longus, peroneus tertius), the lateral compartment (peroneus longus, peroneus brevis), the superficial posterior compartment (soleus), and the deep posterior compartment (tibialis posterior and flexor hallucis longus). Both the posterior and medial malleolus are part of the distal end of the tibia. This article focuses on the shaft of the fibula, which can be located between the neck of the fibula, the narrowed portion just distal to the fibular head, and the lateral malleolus, which in concert with the posterior and medial malleoli, form the ankle joint. There are several distinct portions of the fibula in terms of structure, including the head, neck, shaft, and the distal end termed the lateral malleolus. There is very limited mobility between this syndesmosis. The fibula and tibia connect via an interosseous membrane, which attaches to a ridge on the medial surface of the fibula.

At its most proximal part, it is at the knee just posterior to the proximal tibia, running distally on the lateral side of the leg where it becomes the lateral malleolus at the level of the ankle. Located posterolaterally to the tibia, it is much smaller and thinner. The fibula is one of the two long bones in the leg, and, in contrast to the tibia, is a non-weight bearing bone in terms of the shaft. The following article will focus on fractures of the fibula that are proximal to the ankle joint and the treatment of such fractures. One reason for this may be the treatment for the vast majority of isolated fibula shaft fractures is non-operative - this contrasts with the treatment of lateral malleolus fractures, which, although it is part of the fibula, technically, are categorized as ankle fractures and, therefore, have different treatment principles. Although tibia and fibula shaft fractures are amongst the most common long bone fractures, there is little literature citing the incidence of isolated fibula shaft fractures.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
